Bioaco-record
Bio-acoustics to predict host migratory trends for vector born disease aversion

Project
I developed a bioacoustics IoT system for tracking avian species to enhance infectious disease research, using advanced machine learning algorithms and data science for predictive analysis.
Tools & Technologies
Python · Bash · Raspberry Pi · BirdNET · GSM/2G · ThingSpeak · Scipy · ResNet · Cloud APIs
Impact
- Publication in Sensing and Bio-Sensing Research
- Open source Bio-acoustic setup
- 85% Precision
- 98.7% Accuracy
Overview
Bioaco-record is a modular bioacoustic monitoring system I developed and tested to support research into zoonotic disease transmission by tracking the spatio-temporal movement of bird species. The goal: to generate high-resolution wildlife presence data and explore how ecological interactions influence cross-species pathogen spillover.
Problem
Zoonotic diseases are often driven by biodiversity dynamics, but researchers lack scalable, field-ready tools to passively monitor animal presence in real time. Existing methods are either manual, invasive, or limited in scope.
Solution
I engineered an IoT-powered, solar-ready device capable of:
- Capturing environmental bioacoustic data from birds in real time
- Running on-device ML inference using BirdNET, a ResNet-based classifier
- Transmitting classification results via GSM/2G to ThingSpeak, enabling remote monitoring
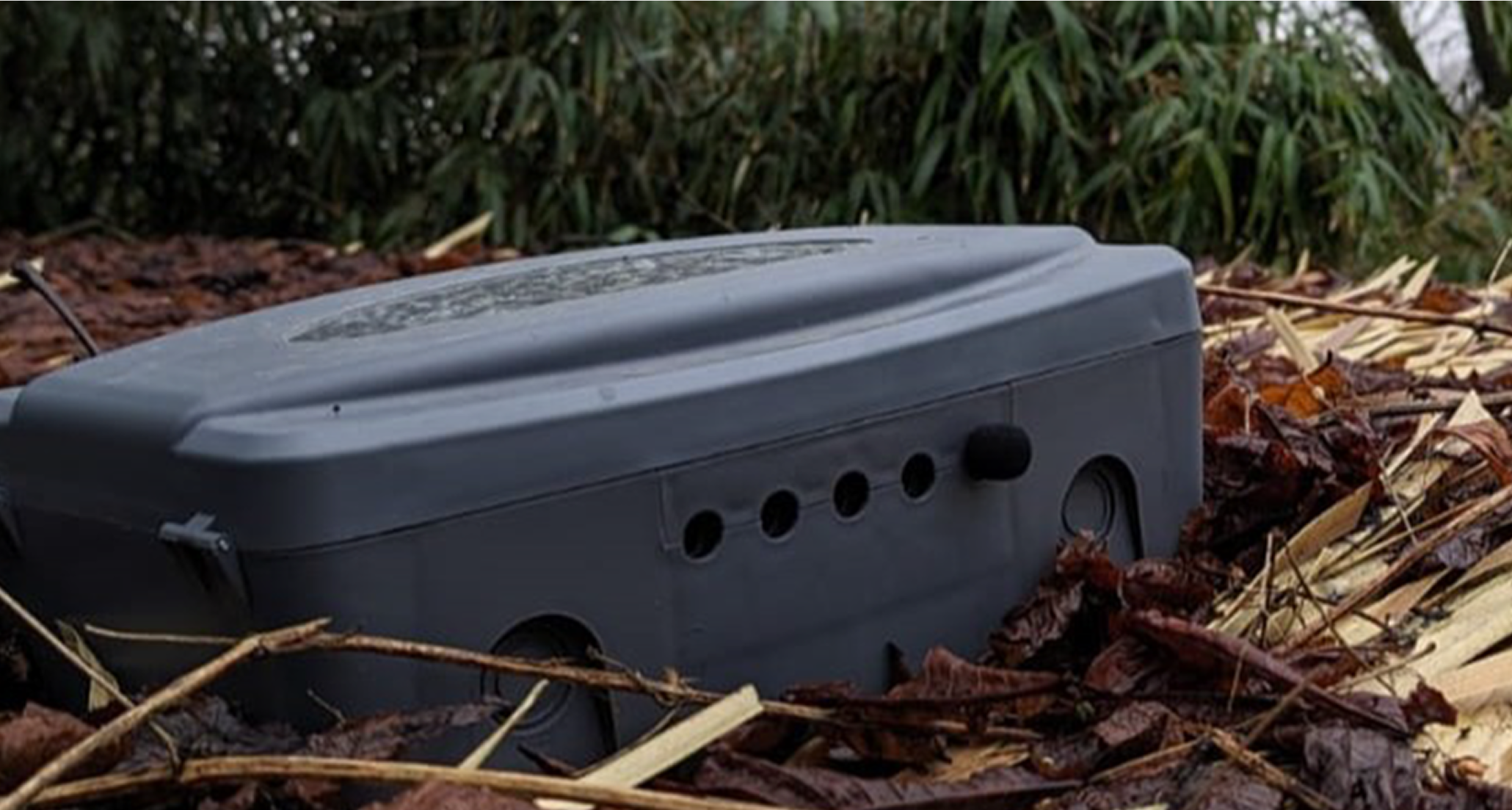
The device, Bioaco-record, is fully modular and designed for deployment in remote or low-power areas using a lead-acid battery (with future plans for solar integration).
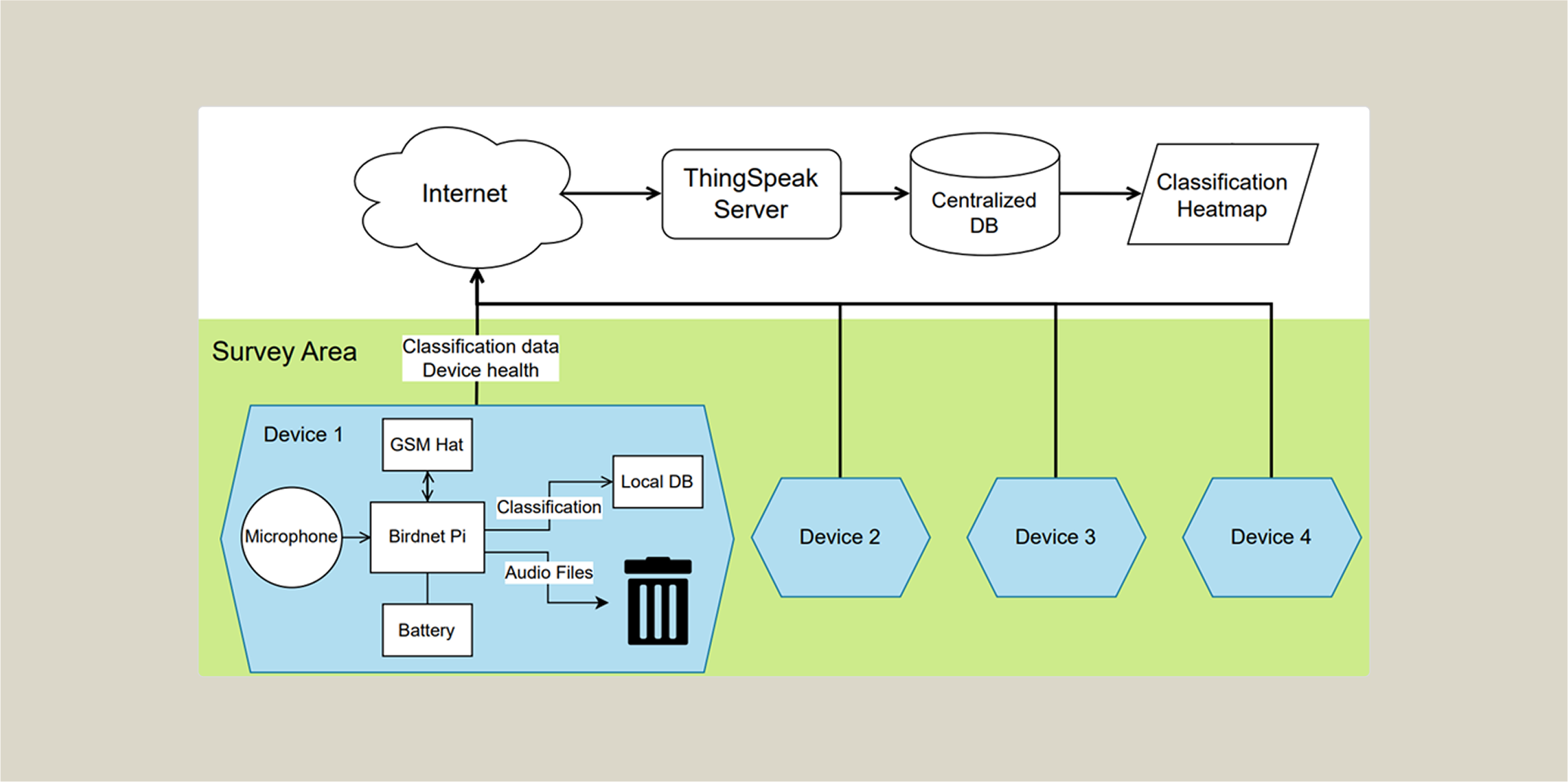
Figure 1: Bioaco-record Flowchart
System Architecture
- Hardware: Raspberry Pi Zero 2W · Sound Card · Microphone · GSM Shield · Lead-acid Battery
- ML Engine: BirdNET-Pi (on-device ResNet classifier)
- Data Pipeline: Audio → Spectrogram → ML Classification → Cloud Upload (via HTTP)
- Remote Visualization: Real-time data analysis on ThingSpeak + spatial heatmaps via scipy.interpolate.griddata (Clough-Tocher interpolation)
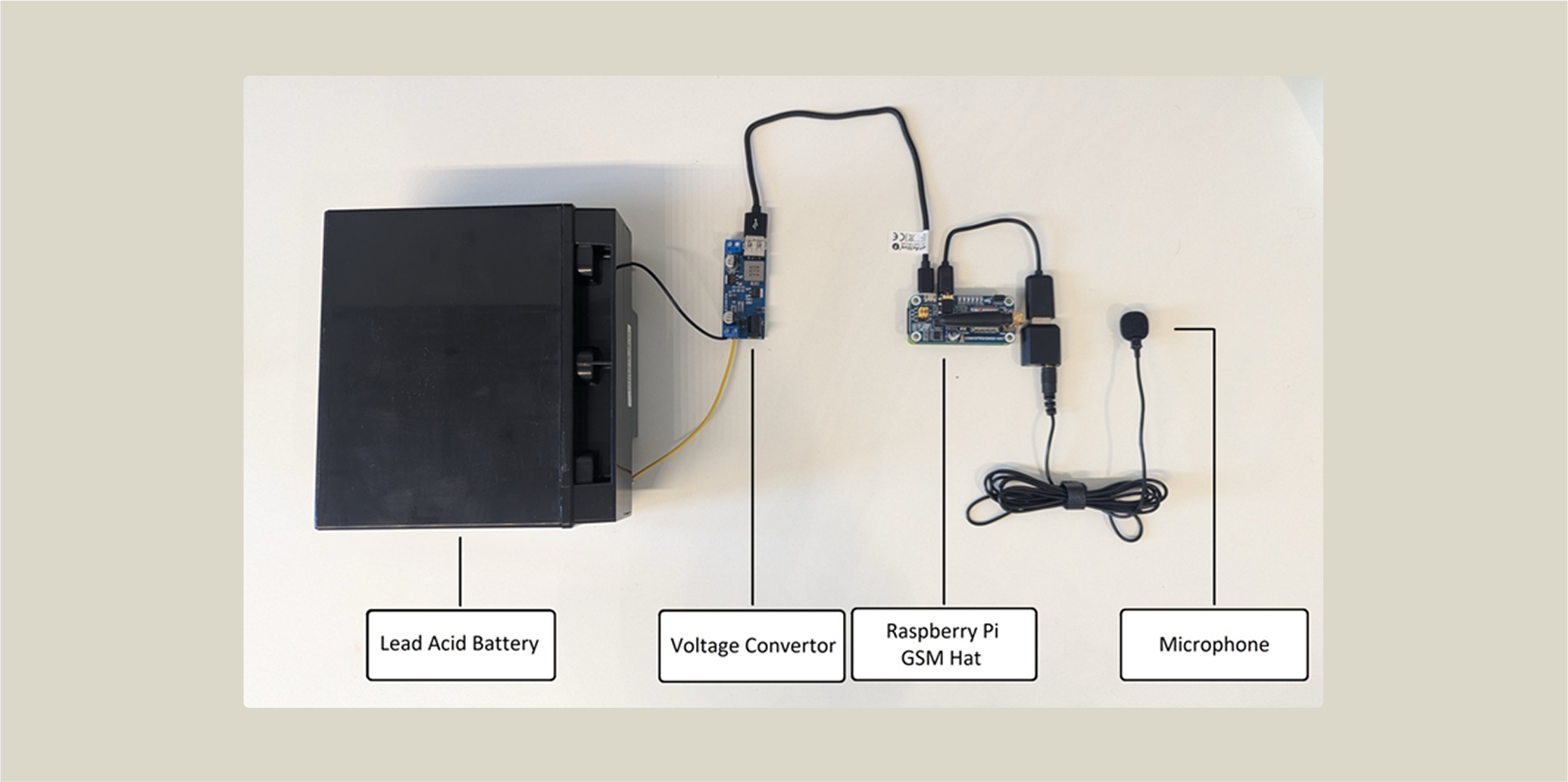
Figure 2: Bioaco-record device
Testing & Validation
We tested the device at Heidelberg Zoo over multiple iterations, refining the setup across four trial runs. Zoo staff verified species classifications, helping validate the system's accuracy for both known and wild bird species.
- Deployment Locations: Sensors placed 70m apart (in and near bird enclosures)
- Validation: Cross-referenced with zoo staff's species knowledge
- Results: Reliable real-time classification and GSM data transmission without WiFi
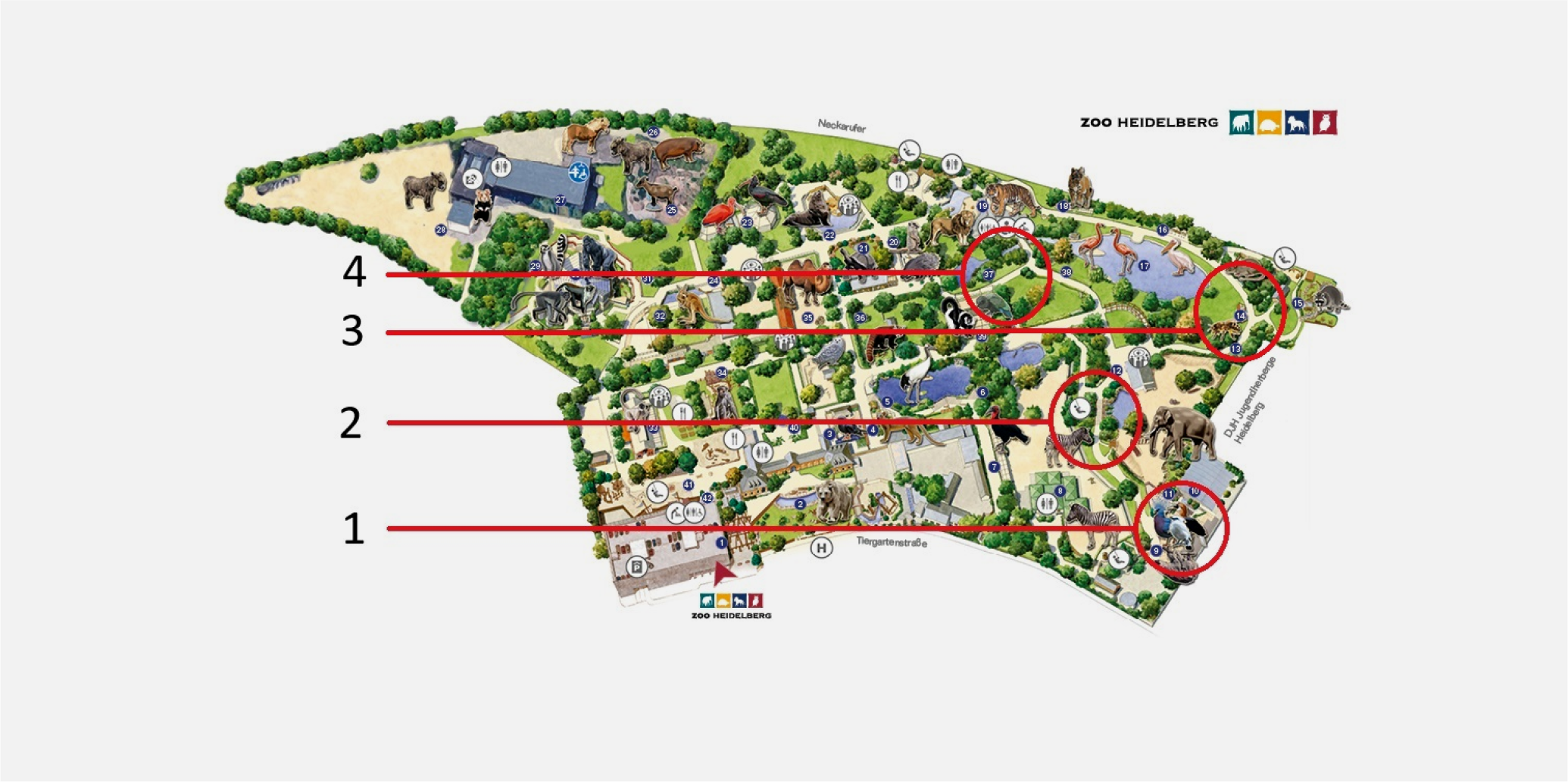
Figure 3: Map of zoo with deployment locations for runs 1-4
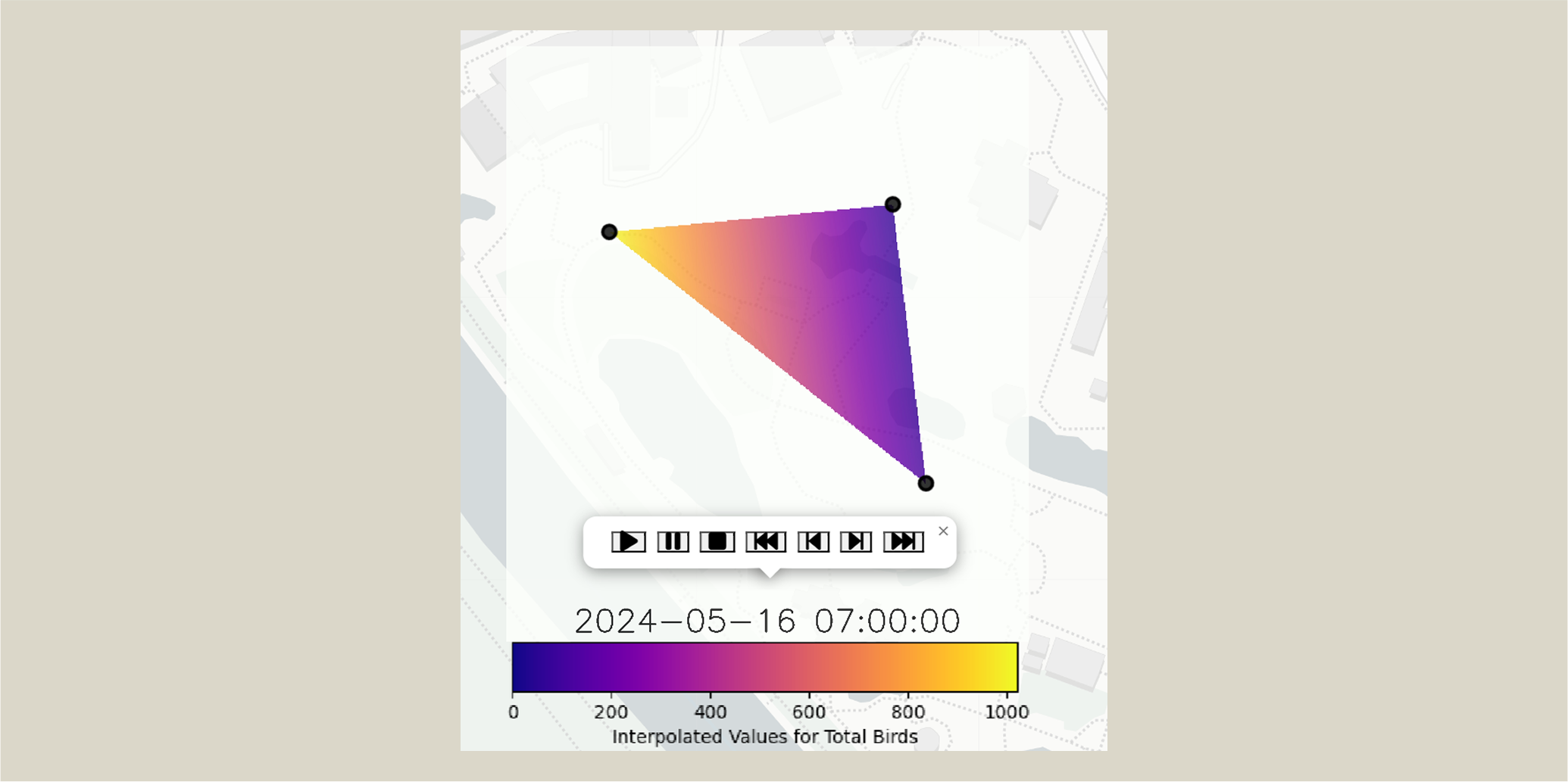
Figure 4: Interpolated heatmap for bird activity
Visualization Output
We produced heatmaps to visualize species presence and activity over time. This helped illustrate how spatial data + sound + ML can inform disease ecology by revealing movement trends of potential pathogen hosts.
Impact
Bioaco-record is a step toward scalable, smart biodiversity sensing tools that can:
- Support research on infectious disease spillover
- Offer insights into how environmental changes impact host-pathogen interactions
- Contribute to nature-based solutions for public and veterinary health
This project is a promising foundation for expanding bioacoustics in ecological surveillance and early warning systems.
Next Steps
- Integrate solar charging for true off-grid operation
- Expand to non-avian species with pluggable ML models (via our Faunanet platform)
- Conduct longitudinal studies across varied ecological zones